Electro Discharge Machining is a process of metal removal from the worksurface due to an erosion of metal caused by electric spark discharge between two electrodes 1)Tool (cathode) and 2)Workpiece (Anode).
This process is also known as spark machining, spark eroding, burning, wire burning, die sinking or wire erosion.
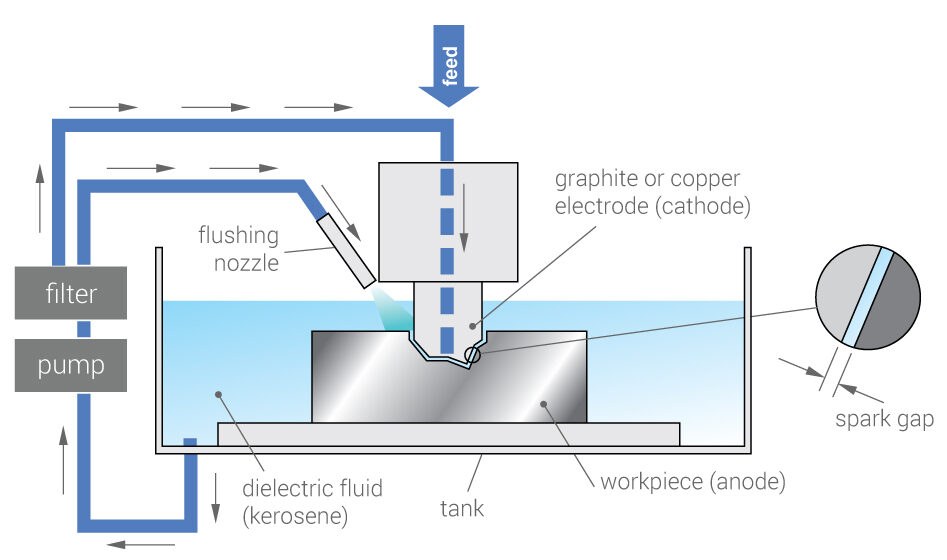
Working Principle: It is an thermoelectric process to erode undesired material from the workpiece.
As the current is supplied, spark is generated between tool and workpiece, the metal in touch with the spark will be evaporated due to high amount of thermal energy. Dielectric fluid is used in the process which insulates the whole setup which prevents melting of extra material by the spark and also acts as a coolant.
Construction:
- Pump
- Filter
- Dielectric fluid
- Tool
- Feed mechanism for tool
Parameters:
- Tool: Cathode (-)
- Workpiece: Anode (+)
- Power Supply: DC
- Voltage: 40 to 300 V
- Current: 0.5 to 400 A
- Spark Gap: 0.0125 to 0.125 mm
- Pulse Duration: 2 to 2000 microseconds
- Material Removal Rate: 800 mm3 to 5000 mm3
- Dielectric Fluid: Paraffin, White spirit, Kerosene and Mineral oil
Applications:
- Drilling very small holes
- Machining complex shapes
Advantages:
- Material hardness does not affect the process
- Process leaves no burrs
- Complex shapes can be cut easily
Limitations:
- Only conductive materials can be machined
- Expensive process



No responses yet